Why Comparing Intel CPUs to AMD X3D Chips Without Equivalent 3D Cache Is Unfair
Tuesday, November 11, 2025Why Comparing Intel CPUs to AMD X3D Chips Without Equivalent 3D Cache Is Unfair
In the fiercely competitive world of high-performance processors, AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology—a 3D stacked cache specially designed to substantially increase last-level (L3) cache—has established a clear performance advantage in gaming workloads. Intel, as of late 2025, lacks a commercially available CPU that matches this technology. As a result, straightforward comparisons of AMD’s X3D CPUs to Intel’s offerings can be misleading or unfair when evaluating gaming and cache-sensitive scenarios.

Understanding 3D V-Cache and Its Gaming Impact
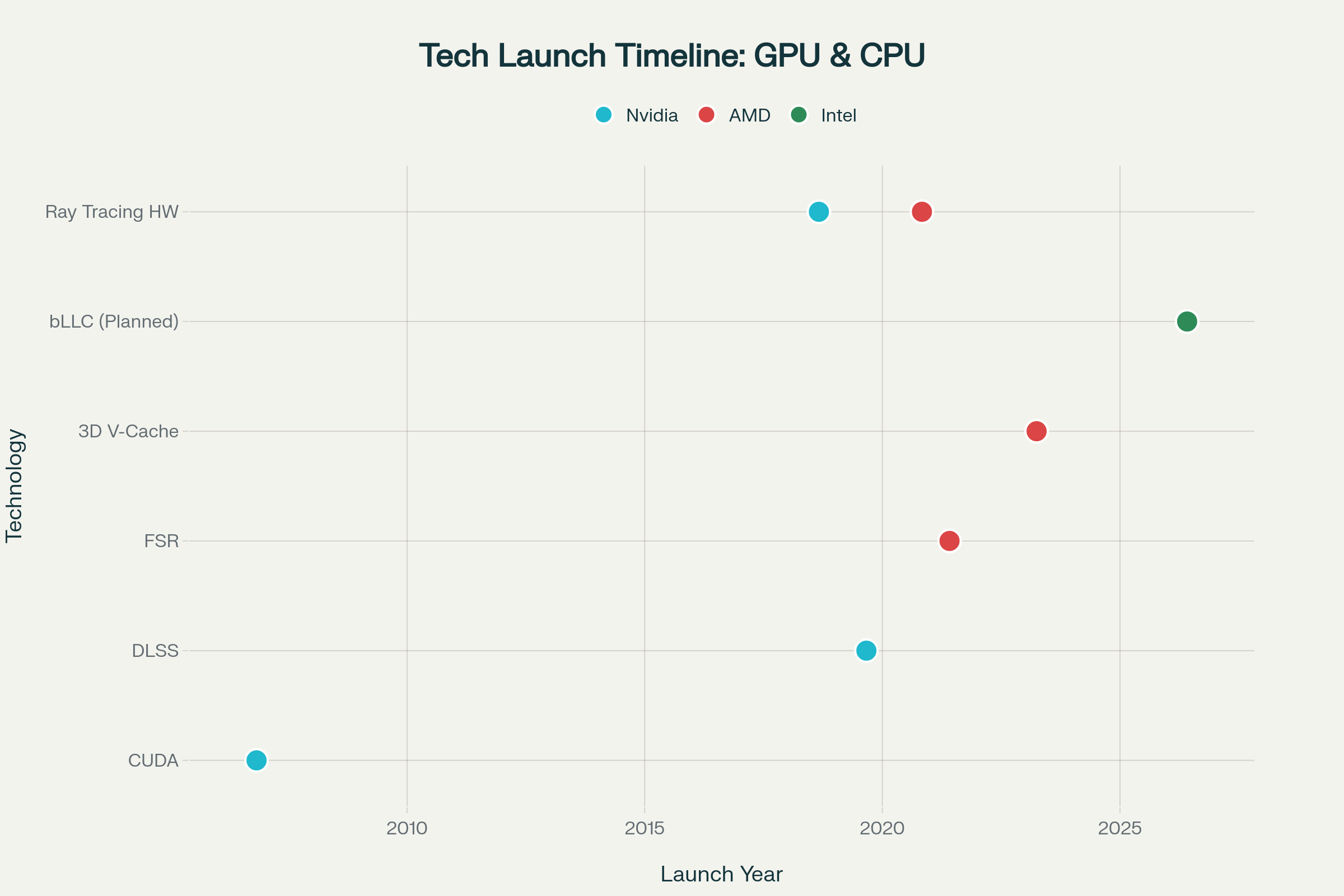
AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology stacks an additional layer of cache vertically on top of the CPU die, significantly increasing cache size without expanding footprint. This cache boost reduces data latency and significantly improves performance in gaming and other cache-sensitive workloads. For example, AMD's Ryzen 9 9950X3D boasts upwards of 144 MB of L3 cache, delivering smoother frame rates especially at 1080p and 1440p resolutions where CPU bottlenecks impact gameplay.
Intel’s latest CPUs do not yet incorporate a stacked cache of this nature, which limits their gaming performance ceiling relative to AMD’s X3D chips. Intel plans to introduce so-called Big Last-Level Cache (bLLC) technology with its next-generation Nova Lake processors, expected in 2026 or 2027, which may bring a similar stacked cache implementation. However, this capability is not yet market-ready or widely available, leaving Intel at a disadvantage today.
Drawing Parallels with Nvidia’s Historical GPU Technology Leadership
- Ray Tracing Hardware: Nvidia introduced dedicated ray tracing cores with RTX GPUs in 2018, delivering real-time ray tracing superior to AMD’s subsequent RDNA 2 implementation in 2020.
- DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling): Nvidia’s AI-driven upscaling technology launched in 2019 gave Nvidia GPUs a substantial frame rate uplift advantage over AMD’s FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR), which arrived in 2021 and initially lagged behind in effectiveness.
- CUDA Ecosystem: Nvidia’s widely adopted CUDA platform for compute and AI workloads created a powerful ecosystem advantage not matched by AMD.
During these periods, Nvidia’s exclusive technologies fundamentally shaped consumer choices and performance leadership despite AMD’s competitive raw performance. Similarly, AMD’s X3D 3D V-Cache delivers a unique gaming performance benefit that Intel currently cannot match.
Market and Consumer Implications
- Unequal Baselines: Comparing Intel CPUs without stacked cache against AMD’s X3D chips is like comparing Nvidia GPUs without ray tracing or DLSS against Nvidia’s RTX lineup—different baseline technologies fundamentally change performance outcomes.
- Contextualized Benchmarks: Reviewers and consumers should consider these architectural differences alongside raw core counts, frequency, and IPC to make informed choices.
- Intel’s Future Roadmap: Intel's planned bLLC in Nova Lake (expected around 2026-27) may close this gap but remains unproven in desktop CPUs currently.
Conclusion
Until Intel releases CPUs with stacked 3D cache comparable to AMD’s X3D, direct comparisons primarily based on gaming and cache-sensitive benchmarks will favor AMD due to this crucial architectural innovation. Historical GPU battles between Nvidia and AMD illustrate how exclusive technologies can create enduring performance gaps. This serves as a reminder that judging a chipset’s true competitiveness requires accounting for unique technology leadership periods.
The timeline below illustrates these technology leadership cycles, showcasing Nvidia’s earlier launches of ray tracing and AI upscaling, AMD’s pioneering 3D V-Cache, and Intel’s upcoming efforts to integrate similar cache technology by 2027.
References are drawn from the latest industry reports and rumors confirming Intel’s plans for big last-level cache, AMD’s current dominance with X3D, and Nvidia’s historical GPU technology leadership.
